Managing Estate Assets During Probate
Key Responsibilities of a Personal Representative in Probate
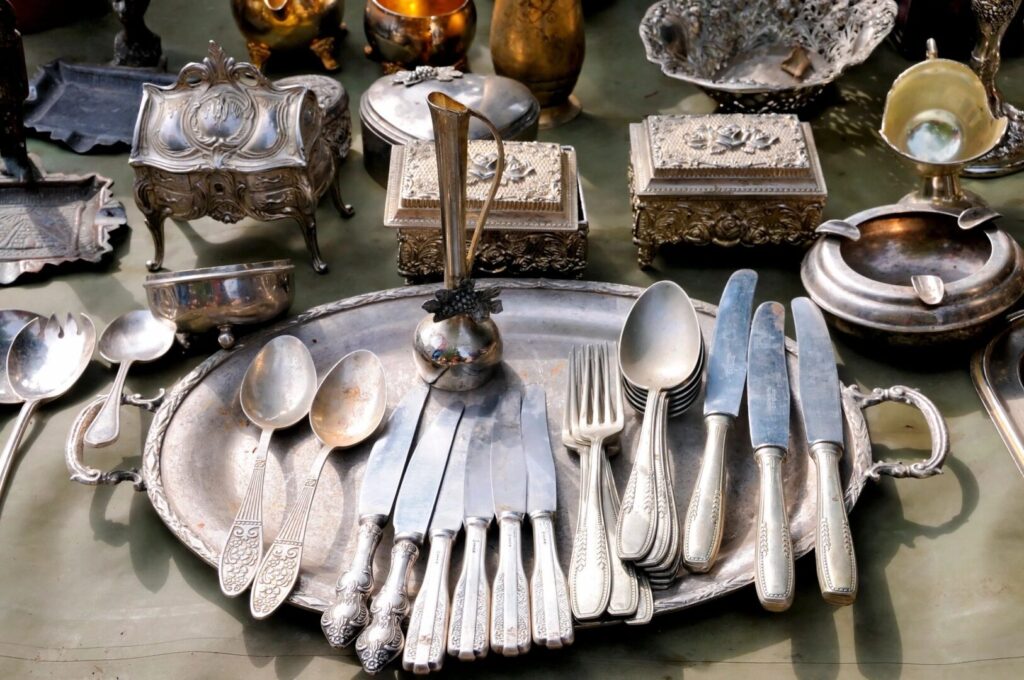
Probate involves numerous tasks that fall under the responsibility of the personal representative (or executor). Their duties include notifying heirs and beneficiaries, alerting creditors, filing estate inventories, and managing various other obligations. A crucial part of their role is gathering all the estate’s assets, which sometimes involves selling them.
Handling Real Estate in Probate
For most people, real estate is their most significant asset. This often includes a primary residence, vacation properties, or investment properties. When a specific will is in place, the personal representative must adhere to its terms regarding real estate distribution. However, in cases where the will doesn’t specify or the estate’s debts exceed its assets, the personal representative might need to sell the property, even against beneficiaries’ wishes. The proceeds from such sales are used to settle estate debts according to Minnesota law’s priority. An important exception applies to homestead properties, which the personal representative cannot sell, mortgage, or lease without the surviving spouse’s consent. Furthermore, homestead properties are often protected from various debt claims.
Authority to Sell Estate Assets
After the decedent’s passing, only the personal representative holds the authority to sell the deceased’s assets. Other individuals lack the legal right to dispose of or sell estate assets without explicit authorization.
Navigating the Probate Process with Expert Assistance
The probate process can be complex and challenging, particularly when managing and selling estate assets. If you need guidance through these intricacies, contact us at (320) 299-4249. Our experienced team can provide the support you need during the probate process.